Working with ARINs Route Registry
This blog post provides a general overview of the Internet Routing Registry. If your network does not use IRR objects, you should have enough information to begin creating your own RPSL objects after after reading this post.
What are Internet Route Registries?
The Internet Routing Registry (IRR) is a distributed routing database development effort. Data from the Internet Routing Registry may be used by anyone worldwide to help debug, configure, and engineer Internet routing and addressing. The IRR provides a mechanism for validating the contents of BGP announcement messages or mapping an origin AS number to a list of networks.
How are IRR Entries Used?
Many large carrier networks automate BGP filtering based on IRR objects. This automation can help to prevent prefix leaks, and advertisements with incorrect AS-PATHs. Because it obviously cannot be run continuously, it can take a few days for everyone who uses IRR to update their routers. When new IP space is first advertised and IRR entries have existed for several days previously, BGP route propagation is much wider and quicker.
Where to Begin?
With ARIN’s IRR, all operations are done through templates via email to the address: rr@arin.net. The entire process is verbosely documented on their website. If you’ve already read this page, and are still scratching your head this post should hopefully clear things up.
To do anything with ARIN’s RR, you need a MNTNER object. These objects are manually approved by ARIN, and also manually entered, so do not expect them to be instant.
Create your MNTNER
Create AND test your MD5 crypted password at this site maintained by ARIN. Your MD5-PW should go on the auth line.
The following is a sample based on my own entry, obviously the password has been changed (it is “cleartextpassword” in this sample).
mntner: MNT-HS-291
descr: Hextet Systems
admin-c: BASCH1-ARIN
tech-c: BASCH1-ARIN
upd-to: theodore@ciscodude.net
mnt-nfy: theodore@ciscodude.net
auth: MD5-PW $1$Lc2Nbj9P$fI9KPhoX4bccGWethuZVp1
notify: theodore@ciscodude.net
mnt-by: MNT-HS-291
referral-by: MNT-HS-291
changed: theodore@ciscodude.net 20150712
source: ARIN
There are 3 auth types: mail-from, md5-pw, and pgp. While PGP is obviously the most secure option, my own attempts (and several people I know) have not resulted in a successful change. So the next best option is md5-pw. To attempt PGP authentication, one needs to first set up their mntner object with mail-from or md5-pw, so it is always necessary to set up mntner with mail-from or md5-pw. I would never recommend mail-from, as anyone could spoof the from address.
The various *-c fields need to be your ARIN contacts. mntner should be “MNT-”" + your ARIN OrgID. Your password should be generated, and not re-used anywhere else, as it will be sent PLAINTEXT in all your requests and modifications afterwards.
Create Route Objects
The following is an example route object (as well as an inetnum object). As you can see the plaintext password is used here. Again, DO NOT RE-USE THIS PASSWORD, for obvious reasons.
route: 192.0.2.0/24
password: cleartextpassword
descr: Sample Route Object
origin: ASxxxxxx
notify: you@you.com
mnt-by: MNT-YOURMNTR
changed: you@you.com YYYYMMDD
source: ARIN
inetnum: 192.0.2.0 - 192.0.2.255
netname: SAMPLE-v4
descr: Sample Inetnum Object
country: CC (2 letter cc code)
notify: you@you.com
mnt-by: MNT-YOURMNTR
admin-c: BASCH1-ARIN
tech-c: BASCH1-ARIN
changed: you@you.com YYYYMMDD
source: ARIN
Validating
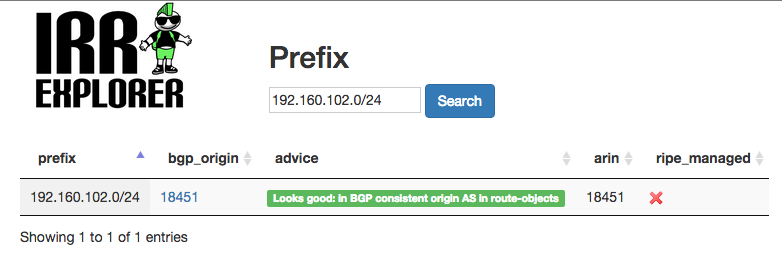
Validate your entries along with your BGP routes using NLNOG’s IRR Explorer. Here is my prefix for example.
Other Entries
autnum
If you operate an AS number and choose to automate your routing policies, it may be helpful to create an AUTNUM object. You need to be fairly large, and peering with other fairly large networks for anyone to start automatically importing your AUTNUM and AS-SET.
as-set
If you give transit to multiple networks, you can specify your down streams within an AS-SET, and use it to specify which routes to announce in your AUTNUM.
inetnum / inetnum6
I’m not entirely sure what these objects are for yet. I’ve created them for HEXTET-v4 and will see what effects it has. It may help with rough Geo Location, perhaps?
route6
Similar to the route object above, a ROUTE6 object is used to describe an IPv6 route.

